Digital Documentation Notes - Class 10 IT 402 NOTES
In this post we will cover class 10 IT code 402 Unit 1 – DIGITAL DOCUMENTATION. We have given the notes for digital documentation here. This unit from the Information Technology subject of class 10 has the highest importance in CBSE board examinations.
Digital Documentation theory notes have been given here, and the practical for Digital Documentation unit have been covered in the videos listed below. By reading these notes for IT code 402, you can score 100 out of 100 in for class 10 CBSE board examination.
These are the latest notes for IT 402 unit 1 digital documentation. Read and Practice from these notes and videos and you are good to go.
Digital Documentation Notes starts from Below!
SESSION 1: CREATE AND APPLY STYLES IN THE DOCUMENT
Style: A style is a set of formats that you can apply to selected pages, text,
frames, and other elements in your document to quickly change their appearance.
OpenOffice.org supports the following types of styles:
Page styles include margins, headers and footers, borders and backgrounds. In Calc, page styles also include the sequence for printing sheets.
Paragraph styles control all aspects of a paragraph’s appearance, such as text alignment, tab stops, line spacing, and borders, and can include character formatting.
Character styles affect selected text within a paragraph, such as the font and size of text, or bold and italic formats.
Frame styles are used to format graphic and text frames, including wrapping type, borders, backgrounds, and columns.
Numbering styles apply similar alignment, numbering or bullet characters, and fonts to numbered or bulleted lists.
Cell styles include fonts, alignment, borders, background, number formats (for example, currency, date, number), and cell protection.
Graphics styles in drawings and presentations include line, area, shadowing, transparency, font, connectors, dimensioning, and other attributes.
Presentation styles include attributes for font, indents, spacing, alignment, and tabs.
Applying styles
Using the Styles and Formatting window(Step by Step)
- Click the Styles and Formatting icon located at the left-hand end of the object bar, or click Format > Styles and Formatting, or press F11. The Styles and Formatting window shows the types of styles available for the OpenOffice (OpenOffice.org) component you are using.
- Click on one of the icons at the top left of the Styles and Formatting window to display a list of styles in a particular.
- To apply an existing style (except for character styles), position the insertion point in the paragraph, frame, or page, and then double-click on the name of the style in one of these lists. To apply a character style, select the characters first.
Using Fill Format mode
Fill format mode is used to apply a style to many different areas quickly without having to go back to the Styles and Formatting window and double-click every time. This method is quite useful when you need to format many scattered paragraphs, cells, or other items with the same style.
-
Open the Styles and Formatting window and select the style you want to apply.
-
Click the Fill Format mode icon to apply a paragraph, page, or frame style, hover the mouse over the paragraph, page, or frame and click.
-
To apply a character style, hold down the mouse button while selecting the characters, clicking on a word applies the character style for that word. Repeat step 3 until you made all the changes for that style.
-
To quit Fill Format mode, click the Fill Format mode icon again or press the Esc key. An important point to note here is that when this mode is active, a right-click anywhere in the document undoes the last Fill Format action. Be careful not to accidentally right click and thus undo actions you want to keep.
Creating New (Custom) Styles
You may want to add some new styles. You can do this in two ways:
- Creating a new style from a selection
You can create a new style by copying an existing manual format. This new style applies only to this document; it will not be saved in the template.
Open the Styles and Formatting window and choose the type of style you want to create.
In the document, select the item you want to save as a style.
In the Styles and Formatting window, click on the New Style from Selection icon.
In the Create Style dialog, type a name for the new style. The list shows the
names of existing custom styles of the selected type. Click OK to save the new style. - Dragging And Dropping To Create A Style
You can drag and drop a text selection into the Styles and Formatting window to create a new style. Select some text and drag it to the Styles and Formatting window. If Paragraph Styles are active, the paragraph style will be added to the list. If Character Styles are active, the character style will be added to the list.
Modifying Styles
OpenOffice.org provides several ways to modify styles (both the predefined styles and custom styles that you create):
- Updating a style from a selection.
- Load or copy styles from another document or template.
Updating A Style From A Selection
- Open the Styles and Formatting window.
- In the document, select an item that has the format you want to adopt as a
style. -
In the Styles and Formatting window,
select the style you want to update (single click, not double-click), then long- click on the arrow next to the New Style from Selection icon and click on Update Style.
Loading Styles From A Template Or Document
You can copy styles by loading them from a template or another document:
- Open the document you want to copy styles into.
- In the Styles and Formatting window, long-click on the arrow next to the New Style from Selection icon, and then click on Load Styles.
- On the Load Styles dialog, find and select the template you want to copy styles from.
- Select the categories of styles to be copied. Select Overwrite if you want the styles being copied to replace any styles of the same names in the document you are copying them into.
- Click OK to copy the styles. You will not see any change on screen.
To copy the styles from another document, click the From File button to open a
window from which you can select the required document.
SESSION 2: INSERT AND USE IMAGES
Images can be added to a document in several ways: by inserting an image file, directly from a graphics program or a scanner, or from the Open Office Gallery.
Inserting An Image File
When the image is in a file stored on the computer, you can insert it into an Open Office document using either of the following methods:
- Drag and Drop
Open a file browser window and locate the image you want to insert Drag the image into the Writer document and drop it where you want it to appear. A faint vertical line marks where the image will be dropped - Insert Picture Dialog
Click in the Open Office document where you want the image to appear.
Choose Insert > Picture > From File from the menu bar.
On the Insert Picture dialog, navigate to the file to be inserted, select it, and click Open.
At the bottom of the dialog are two options, Preview and Link. Select Preview to view a thumbnail of the selected image on the right, so you can verify that you have the correct file. See below for the use of Link. -
Inserting An Image From The Clipboard
Using the clipboard, you can copy images into an Open Office document from another Open Office document and from other programs. To do this: Open both the source document and the target document. In the source document, select the image to be copied Move the mouse pointer over the selected image and press Ctrl+C to copy the image to the clipboard. Switch to the target document Click to place the cursor where the graphic is to be inserted. Press Control+V to insert the image. -
Inserting An Image Using A Scanner
If a scanner is connected to your computer, Open Office can call the scanning application and inserted the scanned item into the Open Office document as an image.
Insert > Picture > Scan > Select Source -
Inserting An Image From The Gallery
To open the Gallery, click on the Gallery icon (located in the right side of the Standard toolbar) or choose Tools > Gallery from the menu bar.
Navigate through the Gallery to find the desired picture.
To insert the picture, click and drag it from the Gallery into the Writer document. You can also right-click on the picture and choose Insert > Copy.
Modifying An Image
We will discuss the use of the Picture toolbar, resizing, cropping, and a workaround to rotate a picture.
Using The Picture Toolbar
When you insert an image or select one already present in the document, the Picture toolbar appears. You can set it to always be present (View > Toolbars > Picture). Picture control buttons from the Picture toolbar can also be added to the Standard Toolbar.
- Graphics mode
You can change color images to grayscale by selecting the image and then selecting Grayscale from the Graphics mode list.
- Flip vertically or horizontally
To flip an image vertically or horizontally, select the image, and then click the relevant icon.
- Filters
Following table includes some of the available filters in OpenOffice
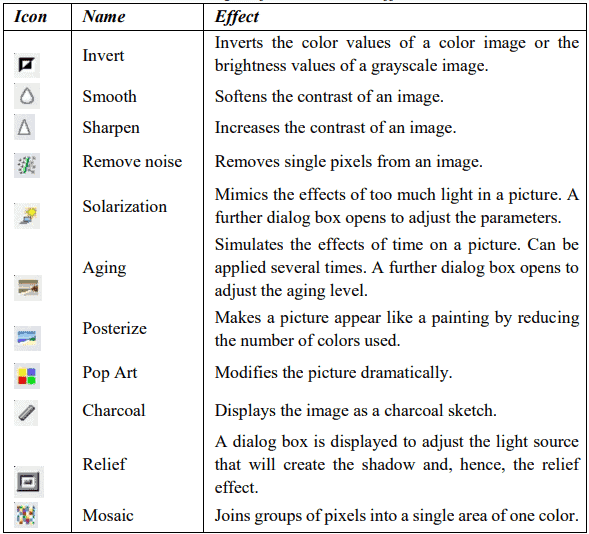
Transparency
Modify the percentage value in the Transparency box on the toolbar to make the image more transparent. This is particularly useful when creating a watermark or when wrapping the image in the background.
Cropping Images
When you are only interested in a section of the image for the purpose of your document, you may wish to crop (cut off) parts of it. To start cropping the image, right click on it and select Picture from the pop-up menu. In the Picture dialog box, select the Crop page.
In the Crop page, you can control the following parameters:
- Keep scale / Keep image size
- Left, Right, Top, and Bottom
- Width and Height
- Resizing an Image
Keep scale / Keep image size
When Keep scale is selected (default), cropping the image does not change the scale of the picture. When Keep image size is selected, cropping produces enlargement (for positive cropping values), shrinking (for negative cropping values), or distortion of the image so that the image size remains constant.
Left, Right, Top, and Bottom
The image is cropped by the amount entered in these boxes. For example, a value of 3cm in the Left box cuts 3 cm from the left side of the picture.
When Keep scale is selected, the size of the image also changes, so in this example the width will be reduced by 3 cm.
When Keep image size is selected, the remaining part of the image is enlarged (when you enter positive values for cropping) or shrunk (when you enter negative values for cropping) so that the width and height of the image remains unchanged.
Width and Height
The Width and Height fields under either Scale or Image size change as you enter values in the Left, Right, Top, and Bottom fields. Use the thumbnail next to these fields to determine the correct amount by which to crop.
Resizing an Image
The inserted image might not fit perfectly into the document if it is too big or too small. In these cases, you can use Writer to resize the image.
Click the picture, if necessary, to show the green resizing handles Position the pointer over one of the green resizing handles. The pointer
changes shape giving a graphical representation of the direction of the resizing. Click and drag to resize the picture.
Release the mouse button.
Rotating a Picture
Writer does not provide a tool for rotating a picture; however, there is a simple workaround:
Open a new Draw or Impress document
(File > New > Drawing or File > New > Presentation).
Insert the image you want to rotate. You can use any of the mechanisms described in “Error! Reference source not found.” on page Error! Bookmark not defined., although there are some slight variations in the position of the menu entries and icons.
Select the image, then in the Drawing toolbar (shown by default at the bottom of the window in Impress and Draw), select the Rotate icon from the Effects tear off toolbar.
Rotate the image as desired. Use the red handles at the corners of the picture and move the mouse in the direction you wish to rotate. By default the picture rotates around its center (indicated by a black crosshair), but you can change the pivot point by moving the black crosshair to the desired rotation center.
To restrict the rotation angle to multiples of 15 degrees keep the Shift key pressed while rotating the image.
Select the rotated picture by pressing Ctrl+A, then copy the image to the clipboard with Ctrl+C.
Finish by going back to the location of the Writer document where the image is to be inserted and pressing Ctrl+V.
Also See:
Digital Documentation Question Bank to score Full!
Digital Documentation Practical Video
Do Read Digital Documentation Notes very thoroughly before going through them.
Creating Drawing Objects
To begin using the drawing tools, display the Drawing toolbar, by click in View > Toolbars > Drawing.
To use a drawing tool:
Click in the document where you want the drawing to be anchored. You can change the anchor later, if necessary.
Select the tool from the Drawing toolbar. The mouse pointer changes to a drawing- functions pointer .
Move the cross-hair pointer to the place in the document where you want the graphic to appear and then click-and-drag to create the drawing object. Release the mouse button. The selected drawing function remains active, so you can draw another object of the same type.
To cancel the selected drawing function, press the Esc key or click on the Select icon (the arrow) on the Drawing toolbar.
You can now change the properties (fill color, line type and weight, anchoring, and others) of the drawing object using either the Drawing Object Properties toolbar or the choices and dialog boxes reached by right-clicking on the drawing object.
Set or Change Properties For Drawing Objects
To set the properties for a drawing object before you draw it:
On the Drawing toolbar (Figure Given Below), click the Select tool.
On the Drawing Object Properties toolbar, click on the icon for each property and select the value you want for that property.
For more control, or to define new attributes, you can click on the Area or Line icons on the toolbar to display detailed dialog boxes.
The default set applies to the current document and session. It is not
retained when you close the document or close Writer, and it does not apply to any other document you open. The defaults apply to all the drawing objects
except text objects.
To change the properties for an existing drawing object:
- Select the object.
- Continue as described above.
You can also specify the position and size, rotation, and slant and corner radius properties of the drawing object:
Right-click on the drawing object and then click Position and Size from the popup menu. The Position and Size dialog box is displayed.
Choose any properties, as required.
Resizing a Drawing Object
The same considerations for resizing an image apply also to resizing an object.
For a scaled resizing, select one of the corner handles and keep the Shift key pressed while dragging the handle to its new position.
For more sophisticated control of the size of the object,
Select Format > Object > Position and Size from the menu bar. Use the Position and Size dialog box to set the width and height independently.
If the Keep ratio option is selected, then the two dimensions change so that the proportion is maintained, allowing for a scaled resizing.
Grouping Drawing Objects
To group drawing objects:
- Select one object, then hold down the Shift key and select the others you want to include in the The bounding box expands to include all the selected objects.
- With the objects selected, hover the mouse pointer over one of the objects and choose Format > Group > Group from the menu bar or right-click and choose Group > Group from the pop-up
Easier Way is by choosing the objects and then using the shortcut key ctrl + G
Positioning Image/Graphics Within The Text
When you add a graphic to a text document, you need to choose how to position it with respect to the text and other graphics.
Positioning of a graphic is controlled by four settings:
Arrangement refers to the placement of a graphic on an imaginary vertical axis. Arrangement controls how graphics are stacked upon each other or relative to the text.
Alignment refers to the vertical or horizontal placement of a graphic in
Anchoring refers to the reference point for the graphics. This point could be the page, or frame where the object is, a paragraph, or even a character. An image always has an anchor point.
Text wrapping refers to the relation of graphics to the surrounding text, which may wrap around the graphic on one or both sides, be overprinted behind or in front of the graphic, or treat the graphic as a separate paragraph or character.
The settings can be accessed in a number of ways, depending on the nature of the graphics:
- From the Format menu, where you can find Alignment, Arrange, Wrap, and Anchor (both for images and drawing objects)
- From the pop-up menu displayed when you right-click on the graphic
- For images, from the Type and Wrapping pages of the Picture dialog Note that you cannot control the arrangement using the dialog box. To open the Picture dialog box, click on the image to select it and then choose Format > Picture or right-click on the graphic and choose Picture on the pop-up menu.
- For drawing objects, from the Position and Size page of the Position and Size dialog To open the Position and Size dialog box, click on the drawing object to select it and then choose Format > Object > Position and Size or right-click on the graphic and choose Position and Size on the pop-up menu. Note that you can only control the alignment and anchoring.
SESSION 3: CREATE AND USE TEMPLATE
What is Template?
A template is a model that you use to create other documents. For Example, If your school makes your school worksheets which have same layout in all with its logo and address. How hard it would be to clone it again and again in the file with same changes. So here you can use Template which will give the logo and basic information to all the files.
Templates can contain:
- Text, Heading, Header/Footer Graphics( Images, Videos, etc) A set of styles
- Default Printer Language Toolbar settings
- Any many such more things.
Creating a Template
You can create your own templates in two ways: from a document, and using a wizard.
Creating A Template From A Document
To create a template from a document:
Open a new or existing document of the type you want to make into a template
Add the content and styles that you want.
From the main menu, choose: File > Templates > Save.
In the new Document wherever you want to use the template follow this:
- In the New template field, type a name for the new template.
- In the Categories list, click the category to which you want to assign the template. The category you choose has no effect on the template itself; it is simply the folder in which you save the template. Choosing an appropriate category makes it easier to find the template when you want to use it.
- Click OK to save the new template.
Creating A Template Using A Wizard
- From the main menu, choose File > Wizards >>template Type
- Follow the instructions on the pages of the wizard. This process is slightly different for each type of template, but the format is very similar.
- In the last section on the wizard you decide where to store the template.
- Finally, you have the option of creating a new document from your template immediately, or manually changing the template.
Setting A Default Template
You can set any template to be the default, as long as it is in one of the folders displayed in the Template Management dialog.
To set a custom template as the default:
- From the main menu, choose File > Templates > The Template Management dialog opens.
- In the box on the left, select the folder containing the template that you want to set as the default, then select the
- Click the Commands button and choose Set As Default Template from the dropdown
Now whenever you open the document you will get the template as the one you set it default.
Resetting the default template
To reset back to default template, simply follow following steps:
- In the Template Management dialog, click any folder in the box on the
- Click the Commands button and choose Reset Default Template from the dropdown
Readers Venue Information Technology Special!
Readers Venue has made lots of Materials for Students to access and learn from. Find the links below:
Digital Documentation Practical Video
Digital Documentation Notes
Electronic Spreadsheet Practical Video
Scroll Down and Continue reading Digital Documentation Notes
SESSION 4: CREATE AND CUSTOMIZE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Basically, here we will learn how to make index in Open Office Document. In Open Office we have a direct feature to make Table of Content. Simply follow the
following steps:
- When you create your document, use the following paragraph styles for different heading levels (such as chapter and section headings): Heading 1, Heading 2, and Heading 3. These are what will appear in your table of contents. You can use more levels of headings, but the default setting is to use only the first three levels in the table of contents.
- Place the cursor where you want the table of contents to be inserted.
- Select Insert > Indexes and Tables > Indexes and Tables
- Change nothing in the Insert Index/Table Click OK.
If you make any changes in headings or if you add some more content and your page number changes than you will need to update the Table of Content. Follow this steps to make changes in the Table of Content:
- Place the cursor within the table of contents.
Right-click and select Update Index/Table from the pop-up menu.
Using the Index/Table tab
You can set Image Attribute in Table of Content/Index. This way you customize the Index.
Setting Basic Attributes
From the Type drop-down list in the Type and title area of the tab, select Table of Contents if it isn’t already selected.
From the drop-down list in the Create index/table area, select Entire document. In the Create from area, check the Outline check box.
In the Create from area, clear the Index marks check box.
Adding A Title
If you’d like the table of contents to have a title, enter it in the Title field. (If Writer entered a title in this field automatically, you can change it by simply typing over the value.) To delete the title, clear the Title field.
Protecting Against Manual Changes
To protect the table of contents from being changed accidentally, check the Protected against manual changes check box.
Changing The Number Of Levels
By default, Writer evaluates 10 levels of headings when it builds the table of contents. To change the number of levels evaluated, enter the desired number in the Evaluate up to level spin box.
Assigning Custom Styles
Writer automatically assigns to the table of contents all paragraphs formatted with the default heading styles (Heading 1, Heading 2, and so on). To assign paragraphs formatted with custom styles, follow these steps:
In the Create from area, check the Additional Styles check box. Click the (…) button to the right of the check box. The Assign Styles window opens.
In the Not applied column, click the style that you want to assign to the table of contents.
Use the >> button to move the selected style to the desired outline level. For example, if you want paragraphs formatted with the selected style to appear as top level entries in the table of contents, click the >> button once to move the style into the 1 column. To move the style in the opposite direction, use the << button.
Click OK to save your changes and return to the Index/Table tab. Or, click Cancel to return without saving your changes.
Using The Entries Tab
Use the Entries tab, to format the entries in the table of contents. For each outline level, you can add and delete elements, such as chapter numbers, and you can also apply character styles to individual elements.
To begin, click a level number in the Level column to select the outline level whose elements you want to format. The Structure line displays the elements for entries in that level. Each button on the Structure line represents one element:
- E# — chapter number
- E — entry text.
- T — tab stop.
- # — page number
- LS — start of a hyperlink.
- LE — end of a hyperlink
Each white field on the Structure line represents a blank space.
Deleting Elements
To delete an element from the Structure line, click the button that represents that element and then press the Delete key on your keyboard.
Adding Elements
To add an element to the Structure line, follow these steps:
Place your cursor in the white field to the left of where you want to insert the element.
Click one of the five buttons that are just below the Structure line. (For example, to add a tab stop, click the Tab stop button.) A button representing the new element appears on the Structure line.
NOTE: If you insert a hyperlink, you must indicate both the beginning and end of the link.
Applying Character Styles
To apply a character style to an element on the Structure line:
On the Structure line, click the button that represents the element to which you want to apply a style.
From the Character Style drop-down list, select the desired style. Writer applies the selected style to the selected element.
To view or edit the attributes of a character style, select the style from the
Character Style drop-down list and then click the Edit button
Applying Changes To All Outline Levels
To apply the displayed structure and formatting to all outline levels, click the all button.
Using The Styles Tab
To apply a paragraph style(Its a type of style, Recall it by going to 1st page) to an outline level, follow these steps:
In the Levels list box, select the desired outline level by clicking it.
In the Paragraph Styles list box, click the paragraph style that you want to apply.
Click the < button to apply the selected paragraph style to the selected outline level.
Using The Background Tab
Use the Background tab, to add color or a graphic to the table background.
To add color to the background of the table of contents, simply click the desired color in the color grid. (Look at the below image).
Adding A Graphic
From the As drop-down list, select Graphic. The Background tab displays the graphics options.
Click the Browse button. The Find Graphics window opens.
Find the graphic file that you want to use and then click the Open button. The Find Graphics window closes and the selected graphic appears in the graphic preview box on the right-hand side of the Background tab. (If you don’t see the graphic, check the Preview check box underneath the graphic preview box.)
In the Type area of the Background tab, choose how you want the background graphic to appear:
To position the graphic in a specific location in the background, select Position and then click the desired location in the position grid.
To stretch the graphic so that it fills the entire background area, select Area.
To repeat the graphic across the entire background area, select Tile.
Updating A Table Of Contents
To update a document’s table of contents when changes are made to the document:
Click anywhere in the table of contents and then right click. The context menu appears.
From the context menu, choose Update Index/Table. Writer updates the table of contents to reflect the changes in the document.
Deleting A Table Of Contents
To Delete the Table of Contents, right click on the table and then choose Delete Index/Table. Writer would delete the Table of Content.
Thanks
Thanks sir so much
Thanks so much
Thank you
Thank you
These notes were very helpful with the help of these notes I scored 49/50 in my PT
Thank you so much for your help sir! These notes were very helpful to understand every concept properly.
Thanks for help
really helpful !!
thank youuuuuu
i think your voice matches to sunlike study guy